RFID stickers are the most common RFID tags and the most economical way of RFID application at present. RFID sticker has the advantages of low cost, soft and light, easy to stick, high production and use efficiency, and can be mass production and printing.
RFID sticker is usually composed of film, covering material, RFID Inlay, an adhesive layer, and release paper. How to choose the materials for each layer is also a science. Figuring out the structure and material is crucial for us to fully understand the RFID sticker and choose the right RFID sticker for our application.
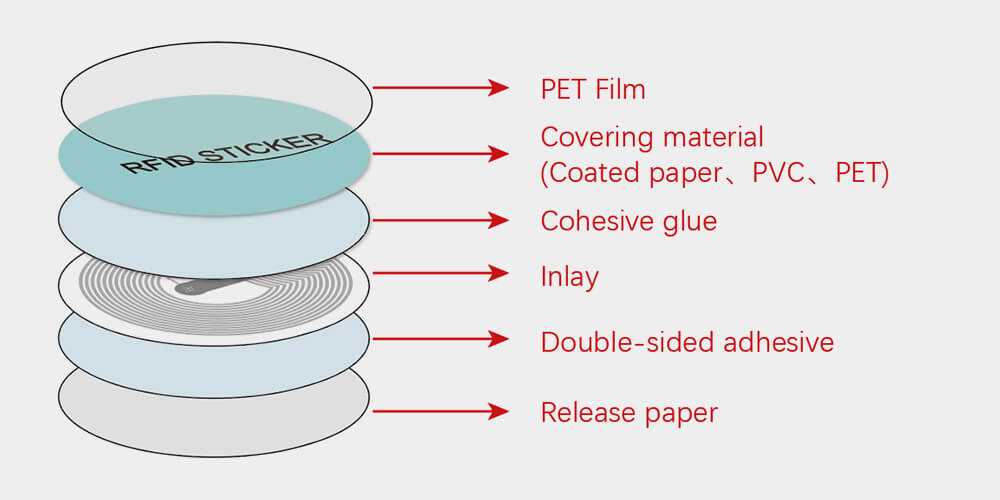
Film
The film is usually the top layer of an RFID tag. There are four kinds of film commonly used for RFID stickers: BBOP film, PET transparent film, PVC film, and PE protective film. Different films have different properties, which you can choose according to the application environment and requirements.
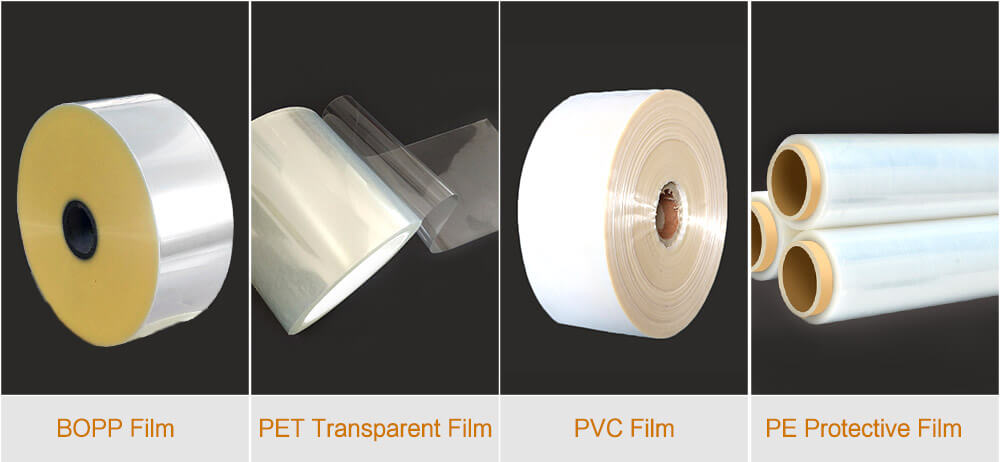
1、BOPP Film
BOPP film is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and features high tensile strength, impact strength, rigidity, strong toughness, and good transparency.
However, the surface energy of BOPP film is low, and corona treatment is required before gluing or printing. In addition, BOPP film is easy to accumulate static electricity, no heat sealing, not suitable for glue dropping, but it is common for coated paper digital printing.
2、PET Transparent Film
PET film features good transparency, gloss, chemical corrosion resistance, and resistance to 150℃ high temperature. Besides, it has excellent mechanical properties. Its strength and toughness are the best of all thermoplastics, and its tensile strength and impact strength are much higher than general films. The film is printable and can be used on surface of RFID epoxy labels.
But PET film is not resistant to strong alkali and prone to static electricity.
3、PVC Film
PVC film is mainly composed of PVC, but there are some other ingredients to enhance its heat resistance, toughness, ductility, etc. Its temperature resistance is about 80 ℃. Compared to the ordinary adhesive film, PVC film is not easy to fall off, owning to using a special vacuum film press at 110℃ temperature to adhere to the surface of the plate. PVC film is printable and can able to use on the surface of RFID epoxy labels.
Disadvantages: not easy to decompose, not environmentally friendly.
4、PE Protective Film
The protective film is made of special polyethylene (PE) plastic film as the substrate. According to density difference divided into high-density polyethylene protective film, medium density polyethylene, and low-density polyethylene. PE protective film features excellent flexibility, environmentally-friendly, and recyclable. It can prevent the tag’s surface from being polluted, corroded, or scratched during packaging production.
Disadvantage: heat resistance is poor (60-70 ℃).
Covering Material
The surface material is the carrier of the sticker, which needs to have good ink acceptance performance. There are many kinds of surface materials, but there are mainly the following four kinds of surface materials for RFID sticker:
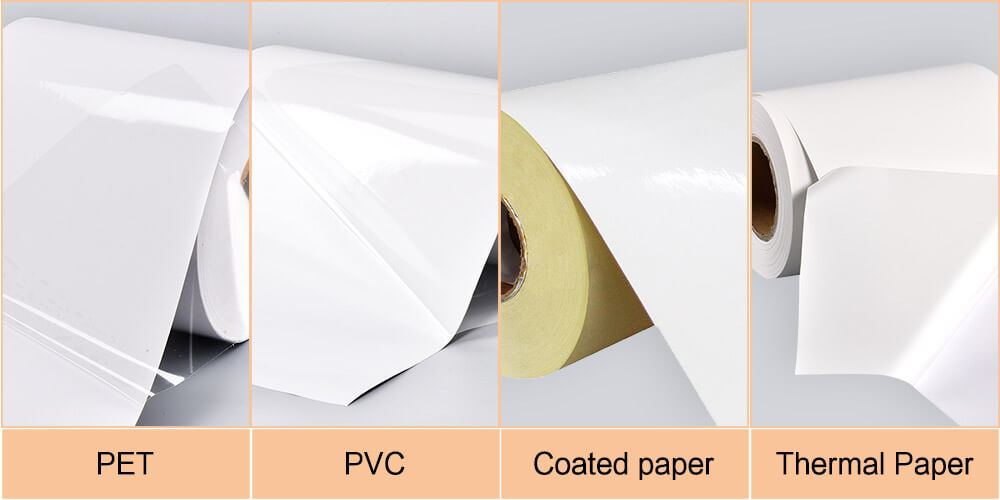
1、PET
PET has the characteristic of light-proof, eco-friendly, tear resistance, high-temperature resistance, and can withstand the harsh environment and chemicals corrosion. Besides, PET paper has good natural degradable, suitable for making various durability labels used in outdoor and other applications that required high quality and durability.
PET RFID stickers have two forms: sheets and rolls. The commonly used thickness of the sheet is 0.1mm or 0.125mm, and the roll is 0.06mm or 0.125mm. PET RFID sticker has a better temperature resistance than PVC RFID sticker. If you want to print on the PET RFID sticker, it needs to add a film.
2、PVC
PVC is similar to PET in performance. Compared with PET, PVC has good flexibility and soft feel, and its cost is lower than PET. PVC is often used in jewelry, clocks, electronics, metal industry, and other high-end occasions. However, PVC degradability is poor that will harm the environment. As same as PET, if you want to print on it, adding a film is necessary.
3、Coated Paper
Coated paper is a commonly used material for RFID sticker, and the thickness is generally around 80g. It is neither waterproof nor oil proof and can be torn easily. But it is economical and practical, very suitable for applications that do not need labels to be kept for a long time.
4、Thermal Paper
Thermal paper is a kind of paper treated by high thermosensitive coating, which can be used for thermal printer printing. Regular thermal paper is not suitable for long-term storage, but good thermal paper can last 30 years or more. Like coated paper, it is not waterproof, oil-proof, and can be torn. It is widely used in supermarket electronic scale labels, chemical laboratories, freezers shelves, etc.
The easiest way to test thermal paper: scratch the paper with your fingernails, leaving a black scratch.
Inlay
The inlay is the core part of the RFID sticker. Inlay gives RFID technology to stickers, which can achieve functions that ordinary stickers cannot, such as identification, tracking, batch reading, etc. Without it, the RFID sticker is just a normal label. According to the frequency, inlays can be divided into the following three categories.
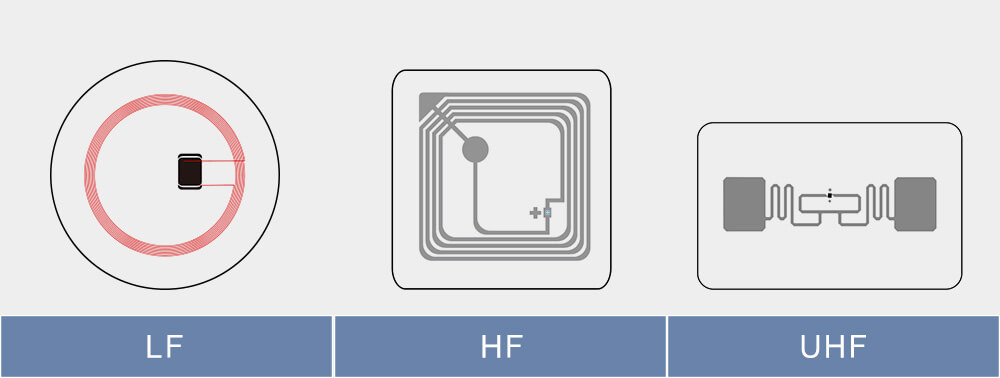
1、Low Frequency Inlay
125 kHz Inlay is composed of copper coils and low-frequency chips. The copper coil is very thin and easy to scrap. Because the antenna and module are not easy to bend and affect the appearance, low-frequency RFID products in the market are mostly encapsulated with hard materials, such as cards, key chains, ABS, etc. and rarely used for flexible labels or RFID stickers.
2、High Frequency Inlay
The 13.56MHz inlay consists of a high-frequency chip and an etched aluminum antenna or copper coil. And the thickness of HF inlay is 0.08mm. The performance of copper wire is similar to that of the etched aluminum antenna, but the copper wire has better electrical conductivity while etching aluminum has obvious advantages in production and delivery time. For RFID cards, then both can be used, but for RFID stickers, then only the etched aluminum antenna inlay can be used.
3、Ultrahigh Frequency Inlay
UHF Inlay is generally composed of UHF chips and dipole antennas, and most UHF antennas are symmetrical. And the thickness of UHF inlay is 0.05mm. UHF RFID sticker works on 860~960MHz and meets the Gen 2 Class 1 & 18000-6C or 6B protocol, suitable for clothing label, logistics tracking, document filing management, library management, etc.
Adhesive
The adhesive is an important part of RFID stickers, making RFID stickers have the ability to attach the objects. Different adhesives have different properties. The best adhesive features uniform coating amount, low cementation rate, thin coating layer, and good viscosity.
1、Classification of Adhesives
According to the performance: permanent adhesive; Restick adhesive; Low-temperature adhesive; Removable adhesive
According to the technology: solvent (commonly known as oil glue); Water solubility (commonly known as water glue); Hot melt adhesive
2、Matters Needing Attention
RFID stickers can be applied to a variety of materials such as glass, metal, cardboard, and plastic. Therefore, it is necessary to choose a suitable adhesive to ensure its good use effect. How to choose? You must consider the material and shape of the object you are pasting, the condition of the labeled surface, and the environment you are using. For example, a rough surface requires a viscous adhesive.
Release Paper
Release paper with an oily surface has an isolation effect on the adhesive to ensure the facestock can be easily peeled off from the release paper. There are three kinds of release paper used for RFID sticker: Glassine, Kraft Paper, and transparent PET.
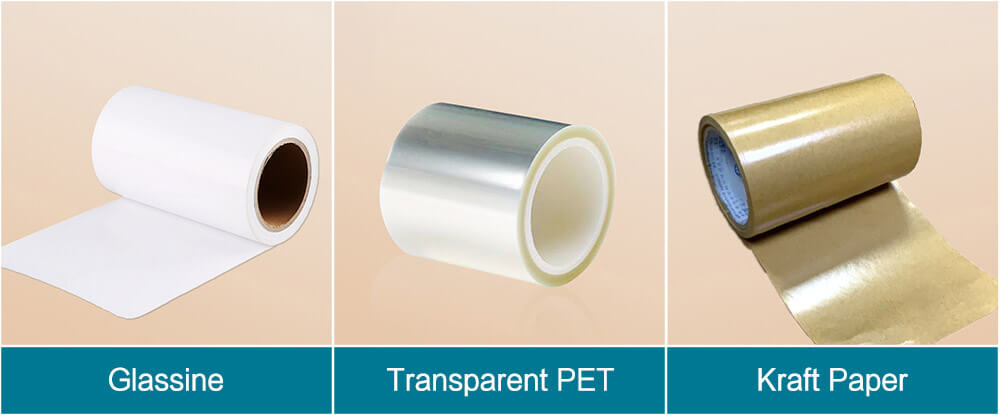

Glassine Paper: Dense and uniform texture, good internal strength and transparent, and is a commonly used material for making bar code labels. Its common colors are blue and white. The thickness is 65mm and 90mm, used for package delivery.
Kraft Paper: used for slicing printing, opaque, commonly seen in yellow and white.
Transparent PET: the back glue is flat; you can check the back glue.
According to the release force, it can be divided into light stripping (within 10g); Middle stripping (10-30g); Re-stripping (30-60g).
